1. Understanding Flicker: Definitions and Standards
Flicker refers to rapid, repetitive fluctuations in light output caused by unstable current supply. According to CIE TN 006-2016, flicker becomes imperceptible to humans when frequencies exceed 125Hz. Low-voltage LED strips (12V/24V DC) are generally flicker-resistant but may exhibit issues due to poor design or incompatible components.
2. Core Causes of Flicker in Low-Voltage LED Strips
2.1 Low-Quality Power Supplies
- AC/DC Ripple: Cheap adapters with insufficient rectification produce residual AC ripple (e.g., 100Hz ripple in 50Hz grid regions).
Example: Testing shows a 12V adapter with 1.2V peak-to-peak ripple causes a flicker index of 0.15 (vs. safe threshold <0.05).
- Voltage Drop: Uncompensated voltage loss in long strips (>5 meters) destabilizes constant-current drivers, triggering flicker.
2.2 PWM Dimming Limitations
- Low-Frequency PWM: Dimming signals below 200Hz create visible flicker, especially at <30% brightness.
- Harmonic Interference: RGBIC strips using overlapping PWM channels may generate harmonic resonance (e.g., 1kHz + 3kHz signals).
2.3 Incompatible Control Systems
- Legacy Controllers: Non-smart controllers lack high-frequency PWM or hybrid dimming, increasing flicker risks.
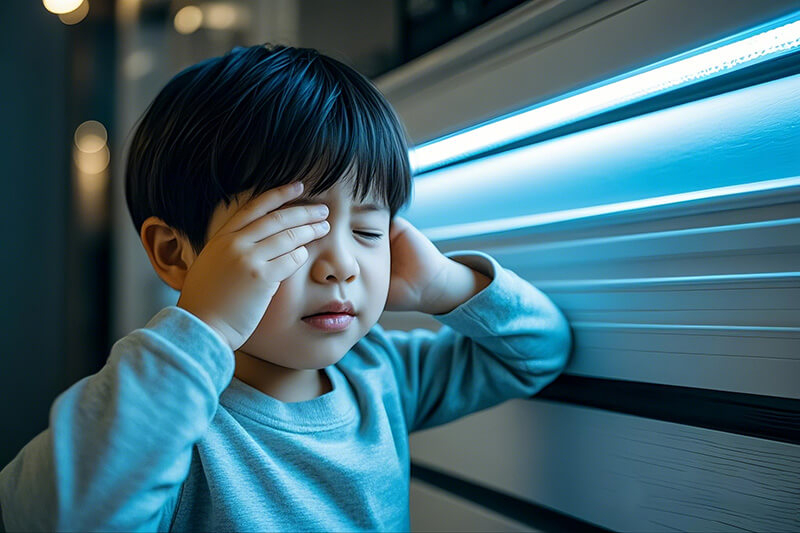

3. Health Risks and Detection Methods
3.1 Documented Impacts
- Short-Term Exposure: Eye strain, migraines (IALD studies show 15% increased intraocular pressure at 120Hz flicker).
- Long-Term Risks: Accelerated myopia progression in children, 3x higher seizure risk for photosensitive individuals.
3.2 Flicker Measurement Tools
- Oscilloscope Testing: Measures waveform frequency and modulation depth (compliance: IEEE 1789-2015, <8% modulation).
- Smartphone Cameras: Detect sub-500Hz flicker via rolling stripes in video mode.
4. Engineering Solutions for Flicker Elimination
4.1 Hardware Optimization
- High-Performance Drivers: Use constant-current drivers with <1% ripple (e.g., TI TPS92662) and >60dB ripple rejection.
- High-Frequency PWM: Adopt >3kHz PWM (DMX512-compatible) or hybrid dimming (PWM + CCR).
4.2 System Design Best Practices
- Voltage Compensation: Install power injection points every 5 meters (12V strips) or 10 meters (24V strips).
- Dedicated Circuits: Separate RGBW channels to minimize PWM crosstalk.
4.3 Consumer Guidance
- Certifications: Prioritize strips with TÜV Flicker-Free or IEC/TR 61547-1 certifications.
- Pre-Purchase Testing: Use smartphone screening or request flicker waveform reports.
5. Future Trends: Beyond Flicker Mitigation
By 2026, next-gen LED strips will integrate:
- GaN-Based Power Systems: Reduce adapter ripple to <0.5% via gallium nitride technology.
- AI-Adaptive Dimming: Real-time flicker suppression using embedded current sensors and machine learning.
If you need assistance from professionals, feel free to contact us. We are here to provide you with expert help and support for all your needs. Don't hesitate to reach out to our team for personalized assistance and solutions. We look forward to serving you.